Tubeless tires have no inner tube, while tube tires contain an inner tube to hold air. Tubeless tires are more puncture-resistant.
Tubeless and tube tires serve the same purpose but differ significantly in structure and performance. Tubeless tires integrate directly with the rim, eliminating the need for an inner tube. This design reduces the risk of sudden deflation, making them safer and more reliable.
Tube tires, on the other hand, have a separate inner tube that can be more prone to punctures and sudden air loss. Cyclists and motorists often prefer tubeless tires for their improved durability and maintenance convenience. Understanding these differences can help you make an informed decision based on your specific needs and preferences.

Introduction To Tubeless And Tube Tires
Understanding the differences between tubeless and tube tires is essential for any vehicle owner. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages. Knowing these can help you make an informed decision. This section provides a brief introduction to both types.
Definition Of Tubeless Tires
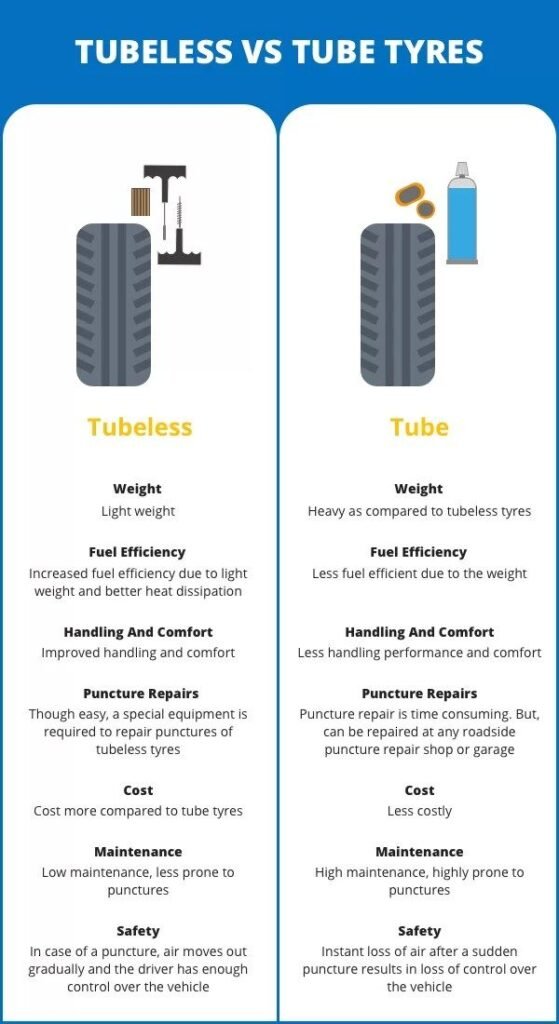
Tubeless tires do not have an inner tube. The tire itself creates an airtight seal with the rim. This design reduces the risk of sudden air loss. Tubeless tires are generally safer and more efficient.
Definition Of Tube Tires
Tube tires have an inner tube that holds the air. The tire and tube are separate components. This traditional design has been used for many years. Tube tires are often easier to repair but can be less efficient.
| Feature | Tubeless Tires | Tube Tires |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | No inner tube | Has inner tube |
| Safety | Less sudden air loss | Higher risk of sudden air loss |
| Efficiency | More efficient | Less efficient |
| Repair | Complex | Simple |
Both types of tires have their specific uses. The choice depends on your needs and preferences. Knowing their differences can help you choose the right tire.
History And Evolution
The history of tires is a fascinating journey. Over the years, tires have evolved significantly. This evolution reflects advancements in technology and materials. Let’s explore the key developments in tire history.
Early Designs
The earliest tires were made of solid rubber. These were used in the late 19th century. They were durable but provided a rough ride. Then came the pneumatic tire, invented by John Boyd Dunlop in 1888. It used an air-filled tube inside a rubber casing. This design offered a much smoother ride.
| Feature | Solid Rubber Tires | Pneumatic Tires |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Solid Rubber | Rubber with Air-filled Tube |
| Comfort | Rough Ride | Smoother Ride |
| Durability | High | Moderate |
Modern Innovations
The 20th century brought significant changes. The invention of the tubeless tire was a major milestone. Tubeless tires do not have a separate inner tube. Instead, they have an airtight seal. This makes them lighter and reduces the risk of flats.
Let’s look at some key differences between tube and tubeless tires:
- Weight: Tubeless tires are lighter.
- Puncture Resistance: Tubeless tires are less likely to go flat.
- Maintenance: Tubeless tires require less maintenance.
These innovations have made modern tires more efficient. They offer better performance and safety. The evolution of tires continues with new materials and designs. Future advancements will likely bring even more improvements.
Construction And Design
Understanding the construction and design of tubeless and tube tires is crucial. It helps in making an informed decision about which type to choose. This section delves into the distinct structural differences between these two tire types.
Structure Of Tubeless Tires
Tubeless tires do not have an inner tube. Instead, they use a continuous rib molded into the tire’s bead. This rib, when pressed against the wheel’s rim, creates an airtight seal. Here are some key features:
- Bead: The bead fits tightly against the rim to prevent air escape.
- Inner Liner: A special lining that maintains air pressure within the tire.
- Valve: The valve is directly attached to the rim, allowing inflation and deflation.
Tubeless tires often have a thicker sidewall. This design helps in maintaining the tire’s structure without an inner tube. They are also less prone to sudden air loss.
Structure Of Tube Tires
Tube tires consist of a tire and a separate inner tube. The inner tube sits inside the tire and holds the air. Key components include:
- Tire Casing: The outer part of the tire, providing the main structural support.
- Inner Tube: A separate inflatable tube inside the tire that holds the air.
- Valve: The valve is part of the inner tube and sticks out through a hole in the rim.
The inner tube can be easily replaced if punctured. Tube tires are simpler in construction but may be more susceptible to punctures.
| Component | Tubeless Tires | Tube Tires |
|---|---|---|
| Inner Tube | None | Present |
| Bead | Seals against rim | Not airtight |
| Valve | Attached to rim | Attached to inner tube |

Performance And Efficiency
Understanding the performance and efficiency of tubeless and tube tires is crucial for making an informed decision. Both types offer different benefits and can impact your riding experience in various ways.
Rolling Resistance
Rolling resistance is a key factor in tire performance. Tubeless tires generally have lower rolling resistance compared to tube tires. This means less energy is lost as the tire rolls, resulting in a smoother ride.
In contrast, tube tires experience higher rolling resistance due to the friction between the tube and tire. This can lead to a slightly more effortful ride.
Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency is another important aspect of tire performance. Tubeless tires are known to be more fuel-efficient. The reduced rolling resistance helps in conserving fuel, making your vehicle more economical.
On the other hand, tube tires may not offer the same level of fuel efficiency. The increased rolling resistance can lead to higher fuel consumption over time.
| Feature | Tubeless Tires | Tube Tires |
|---|---|---|
| Rolling Resistance | Lower | Higher |
| Fuel Efficiency | Better | Less Efficient |
In summary, tubeless tires excel in both rolling resistance and fuel efficiency. They provide a smoother ride and help save on fuel costs. Tube tires might not match up in these areas, but they have their own set of advantages.
Maintenance And Repair
Understanding the differences between tubeless and tube tires is crucial. Maintenance and repair play a vital role in tire longevity and safety. This section delves into the specifics of repairing tubeless and tube tires.
Repairing Tubeless Tires
Tubeless tires are easier to repair. They do not have an inner tube, which simplifies the process. Here is a step-by-step guide for fixing a tubeless tire:
- Locate the puncture using soapy water.
- Remove any debris from the puncture site.
- Insert a tire plug into the puncture.
- Use a plug tool to push the plug into the hole.
- Trim excess plug material with a knife.
- Reinflate the tire to the recommended pressure.
Repair kits for tubeless tires are widely available. These kits include everything needed for a quick fix.
Repairing Tube Tires
Tube tires require more steps for repair. The inner tube must be removed from the tire. Follow these steps:
- Remove the wheel from the vehicle.
- Deflate the tire completely.
- Use tire levers to remove the tire from the rim.
- Take out the inner tube carefully.
- Locate the puncture using soapy water.
- Patch the hole with a tube repair kit.
- Reinstall the tube inside the tire.
- Mount the tire back onto the rim.
- Reinflate the tire to the proper pressure.
- Reattach the wheel to the vehicle.
Repairing tube tires is more time-consuming. You need specific tools and a repair kit for this process.
| Feature | Tubeless Tires | Tube Tires |
|---|---|---|
| Repair Steps | Fewer | More |
| Tools Needed | Plug tool, knife | Tire levers, patch kit |
| Time Required | Less | More |
Both types of tires have their pros and cons. Choose according to your needs and preferences.
Safety And Reliability
Tubeless and tube tires have distinct differences in safety and reliability. Understanding these differences helps make an informed choice. Let’s explore the key aspects of safety and reliability for both tire types.
Puncture Resistance
Tubeless tires offer better puncture resistance. They have no inner tube, which reduces the risk of sudden air loss. When a puncture occurs, the air escapes more slowly. This allows the rider to handle the situation safely.
Tube tires, on the other hand, are more prone to punctures. The inner tube can burst suddenly. This can lead to a rapid loss of air. As a result, tube tires can be less reliable in maintaining air pressure.
| Feature | Tubeless Tires | Tube Tires |
|---|---|---|
| Puncture Resistance | High | Low |
| Air Loss | Slow | Rapid |
Load Handling
Tubeless tires handle loads better. They distribute weight evenly across the surface. This provides a more stable ride. They also maintain better contact with the road.
Tube tires can struggle with heavy loads. The inner tube can shift or move. This can cause instability. Tube tires may also wear out faster under heavy loads.
- Tubeless tires: Even weight distribution, stable ride, better road contact.
- Tube tires: Potential instability, faster wear under load.
In summary, tubeless tires generally offer better safety and reliability. They provide higher puncture resistance and better load handling. Tube tires, though simpler, may fall short in these critical areas.
Cost And Affordability
Understanding the cost and affordability differences between tubeless and tube tires can help you make a better decision. Let’s break down the initial costs and long-term costs to see which option suits your budget.
Initial Cost
The initial cost of tubeless tires is generally higher than tube tires. The reasons include:
- Advanced technology: Tubeless tires use more advanced materials.
- Specialized rims: Tubeless tires need specific rims, adding to the cost.
Tube tires are usually cheaper because:
- Simpler construction: Tube tires have a simpler design.
- Standard rims: They fit on standard rims, which are less expensive.
Long-term Costs
Long-term costs of tubeless tires can be lower due to:
- Fewer punctures: Tubeless tires are less prone to punctures, saving on repairs.
- Better efficiency: They provide better fuel efficiency, reducing fuel costs.
Tube tires might have higher long-term costs because:
- Frequent punctures: Tube tires are more likely to get punctured, needing more repairs.
- Lower efficiency: They can reduce fuel efficiency, increasing fuel expenses.

Suitability For Different Uses
When choosing between tubeless and tube tires, understanding their suitability for different uses is crucial. This section dives into how each tire type performs in various environments and applications.
Off-road Applications
In off-road conditions, tubeless tires offer significant advantages. These tires can run at lower pressures, providing better traction on rough terrains. The absence of a tube reduces the risk of pinch flats, which is essential for rocky paths. Additionally, tubeless tires can self-seal small punctures with sealant, ensuring uninterrupted rides.
On the other hand, tube tires are less perfect for off-road use. They are more prone to pinch flats and require higher pressures to avoid damage. This makes them less efficient on uneven trails. While they can still be used off-road, they don’t offer the same level of performance and reliability as tubeless tires.
Urban And Highway Use
In urban settings, both tubeless and tube tires have their pros and cons. Tubeless tires provide a smoother and more comfortable ride, thanks to lower air pressure. They also reduce the risk of sudden flats, making them safer for city commuting.
Tube tires are more common in urban environments due to their lower cost and ease of maintenance. They are suitable for city rides where road conditions are relatively smooth. However, they may not offer the same level of comfort as tubeless tires.
On highways, tubeless tires excel due to their increased performance at higher speeds. They offer better heat dissipation, reducing the risk of blowouts. The ability to self-seal small punctures ensures fewer interruptions during long drives.
Tube tires can also be used on highways, but they may not perform as well at high speeds. They are more prone to heat buildup, which can lead to blowouts. Regular maintenance and checks are essential for safe highway use.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Is Better, Tube Tire Or Tubeless?
Tubeless tires are generally better. They offer better puncture resistance, lower rolling resistance, and are lighter. Tube tires, however, are easier to repair and cheaper.
Do Pros Use Tubes Or Tubeless?
Pros typically use tubeless tires. They offer better performance, reduced punctures, and improved traction. Tubeless is preferred for racing and competitive cycling.
What Is The Disadvantages Of Tubeless Tyres?
Tubeless tyres can be more expensive to install. They may suffer from sudden air loss. Repairing punctures can be difficult. Special rims are required.
Can Tubeless Tires Go Flat?
Yes, tubeless tires can go flat. They are less prone to punctures but can still lose air due to damage. Regular maintenance helps.
Conclusion
Choosing between tubeless and tube tires depends on your needs. Tubeless tires offer better performance and fewer punctures. Tube tires are easier to repair and cheaper. Consider your riding conditions and budget. Both options have their advantages. Make an informed decision to improve your biking experience.