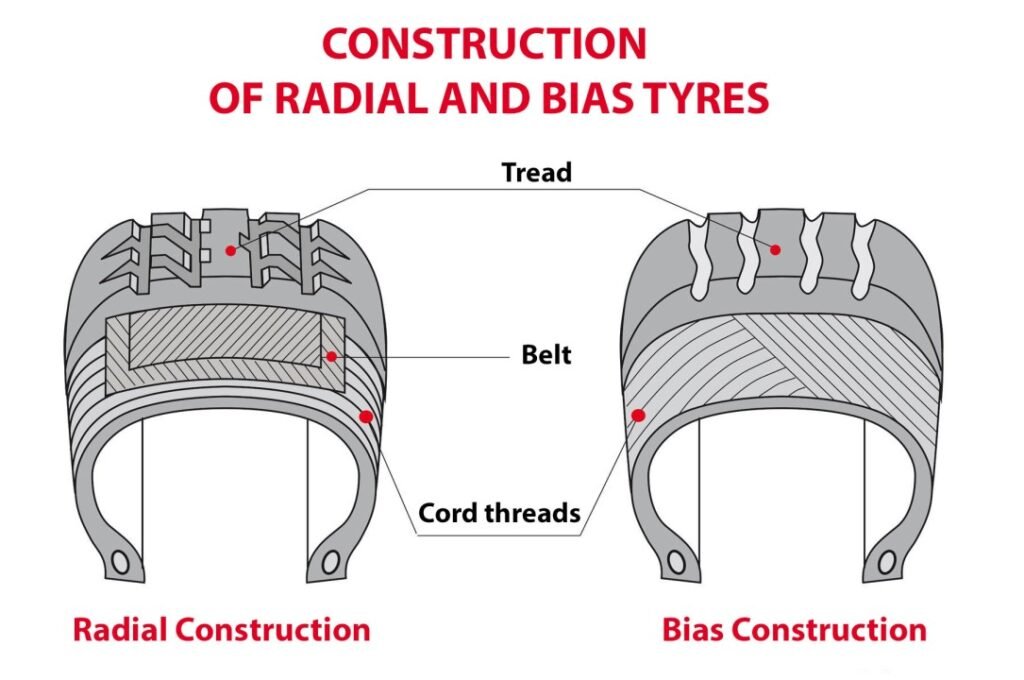
Bias tires have crisscrossed layers of rubber, while radial tires have steel belts running perpendicular to the tread. Radial tires offer better fuel efficiency and handling.
Choosing the right tires is crucial for vehicle performance and safety. Bias and radial tires differ significantly in construction and benefits. Bias tires, with their crisscrossed layers, provide a smooth ride on rough terrains. Radial tires, featuring steel belts, ensure superior traction and fuel efficiency.
Understanding these differences helps in making informed decisions. Radial tires are generally preferred for daily driving due to their better handling and longevity. Bias tires are suitable for off-road conditions and heavy loads. Knowing your driving needs will aid in selecting the appropriate tire type.

Introduction To Tire Types
Tires are vital for any vehicle. They affect safety and performance. Two main types are Bias Tires and Radial Tires. Each type has unique features. Knowing these can help you choose the right tire.
Bias Tires
Bias tires have a unique construction. Their layers are diagonal. This design makes them strong. They are good for rough terrains.
Key Features:
- Diagonal layers
- Strong sidewalls
- Good for off-road
Advantages:
- Durable
- Cost-effective
- Flexible
Disadvantages:
- Less smooth ride
- More heat build-up
- Shorter lifespan
Radial Tires
Radial tires have a different design. Their layers are perpendicular. This makes them flexible. They offer a smoother ride.
Key Features:
- Perpendicular layers
- Flexible sidewalls
- Good for highways
Advantages:
- Smoother ride
- Less heat build-up
- Longer lifespan
Disadvantages:
- More expensive
- Can be less durable
- Not perfect for rough terrains
| Feature | Bias Tires | Radial Tires |
|---|---|---|
| Layer Design | Diagonal | Perpendicular |
| Sidewall Strength | Strong | Flexible |
| Ride Comfort | Less smooth | Smoother |
| Heat Build-Up | More | Less |
| Lifespan | Shorter | Longer |
| Cost | Less expensive | More expensive |
Construction Differences
Understanding the construction differences between bias and radial tires is essential. Both types of tires are constructed differently, affecting performance and durability. Let’s dive into the specifics.
Layer Arrangement
In bias tires, the layers, or plies, are arranged diagonally. Each layer crisscrosses the previous one. The layers form a pattern of overlapping plies. This makes the tire sturdy.
In radial tires, the layers are arranged radially. They run perpendicular to the tire’s circumference. The plies do not crisscross. This arrangement provides flexibility.
Material Composition
Bias tires often use a mix of materials. These materials include nylon and polyester. They increase the tire’s durability. Bias tires are also less flexible.
Radial tires primarily use steel belts. These belts are placed below the tread. Steel belts offer better strength. Radial tires also use polyester, but only in the sidewalls. This combination offers better handling.
| Aspect | Bias Tires | Radial Tires |
|---|---|---|
| Layer Arrangement | Diagonal, crisscross pattern | Radial, perpendicular to the circumference |
| Material Composition | Nylon, polyester | Steel belts, polyester in sidewalls |
These construction differences affect the tire’s performance. Understanding them helps you make better choices.
Performance Comparison
Understanding the differences between bias and radial tires is crucial. Performance can vary significantly, impacting your driving experience. We will explore handling, stability, and tread life.
Handling And Stability
Bias tires have a crisscross construction. This design offers a stiffer sidewall. Stiffer sidewalls can improve handling on rough terrains. They are good for off-road conditions.
On the other hand, radial tires have a flexible sidewall. This flexibility improves ride comfort and handling on highways. Radial tires provide better stability at higher speeds.
| Aspect | Bias Tires | Radial Tires |
|---|---|---|
| Sidewall | Stiffer | Flexible |
| Handling | Better on rough terrains | Better on highways |
| Stability | Lower at high speeds | Higher at high speeds |
Tread Life
Bias tires generally have a shorter tread life. The crisscross construction causes uneven wear. This uneven wear reduces their lifespan.
Radial tires have a longer tread life. Their construction ensures even wear. This even wear extends the tire’s lifespan.
| Aspect | Bias Tires | Radial Tires |
|---|---|---|
| Tread Life | Shorter | Longer |
| Wear Pattern | Uneven | Even |
Ride Comfort
Ride comfort is a significant factor when choosing between bias and radial tires. The construction of each tire type directly affects how they handle vibrations, noise, and shock absorption. Understanding these differences can help you make an informed decision for a smoother driving experience.
Vibration And Noise
Radial tires are known for their superior vibration and noise control. They have flexible sidewalls that reduce road vibrations. This leads to a quieter and more comfortable ride.
Bias tires, on the other hand, have stiffer sidewalls. This construction can lead to more vibrations. These vibrations can translate to a noisier ride.
| Feature | Radial Tires | Bias Tires |
|---|---|---|
| Vibration Control | Excellent | Moderate |
| Noise Levels | Low | High |
Shock Absorption
Radial tires excel in shock absorption. Their flexible sidewalls and tread design help in absorbing shocks from road irregularities. This results in a smoother ride.
Bias tires have a different construction. Their stiffer sidewalls do not absorb shocks as effectively. This can lead to a rougher ride.
- Radial Tires: Better shock absorption due to flexible sidewalls.
- Bias Tires: Poor shock absorption due to stiffer sidewalls.
Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency is a major factor when choosing tires. Bias tires and radial tires impact fuel efficiency differently. Understanding these differences can help you make informed decisions.
Rolling Resistance
Rolling resistance refers to the energy lost when a tire rolls. Radial tires have lower rolling resistance. This is because their construction allows for more flexibility. Bias tires have higher rolling resistance due to their rigid structure.
The table below shows a comparison of rolling resistance between the two types:
| Tire Type | Rolling Resistance |
|---|---|
| Radial Tires | Low |
| Bias Tires | High |
Fuel Consumption
Lower rolling resistance in radial tires leads to less fuel consumption. Vehicles with radial tires often have better fuel economy. Bias tires consume more fuel due to their higher rolling resistance.
Consider the following points:
- Radial tires: Save on fuel costs
- Bias tires: Higher fuel consumption
Choosing the right tire can significantly impact your fuel efficiency.
Usage Scenarios
Understanding the differences between bias and radial tires helps choose the right tire for specific needs. Each tire type has unique features making it suitable for certain situations. This section explores the perfect usage scenarios for both bias and radial tires.
Off-road Applications
Bias tires are excellent for off-road applications. Their thick sidewalls provide durability and resistance to punctures. Bias tires offer better traction on rough terrains. They are perfect for construction and agricultural vehicles. Bias tires also work well in muddy and sandy conditions.
Radial tires, on the other hand, have flexible sidewalls. They are not as durable in off-road conditions. Radial tires can suffer damage from sharp objects. They are better suited for smoother surfaces. Bias tires outperform radial tires in off-road scenarios.
Highway Driving
Radial tires are perfect for highway driving. They provide a smoother and more comfortable ride. Radial tires have better fuel efficiency due to lower rolling resistance. They offer superior traction on paved roads. Radial tires also have a longer tread life.
Bias tires are less suitable for highway driving. Their thick sidewalls create more heat and noise. This results in a less comfortable ride. Bias tires also have higher rolling resistance. This leads to reduced fuel efficiency. For long highway journeys, radial tires are the better choice.
| Feature | Bias Tires | Radial Tires |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High in off-road conditions | Lower in off-road conditions |
| Ride Comfort | Less comfortable | More comfortable |
| Fuel Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
| Tread Life | Shorter | Longer |
| Traction on Rough Terrain | Better | Worse |
| Heat and Noise | Higher | Lower |
Cost Implications
Understanding the cost implications of bias and radial tires is crucial for informed decisions. This section delves into the initial purchase price and long-term value of both types of tires.
Initial Purchase Price
The initial purchase price of bias tires is usually lower. These tires are cheaper to manufacture. This makes them more affordable for budget-conscious buyers.
Radial tires, on the other hand, have a higher initial cost. Their complex construction and advanced materials increase the price. If you seek immediate savings, bias tires might be your choice.
Long-term Value
When considering long-term value, radial tires often come out ahead. They offer better fuel efficiency. This means you spend less on gas over time. Radial tires also have a longer lifespan. They can last up to 20% longer than bias tires.
Though the initial cost is higher, radial tires save money in the long run. They provide better value for frequent drivers and long-distance travelers.
| Feature | Bias Tires | Radial Tires |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Purchase Price | Lower | Higher |
| Fuel Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
| Lifespan | Shorter | Longer |
In summary, bias tires are cheaper initially but may cost more over time. Radial tires cost more upfront but offer better long-term savings. Choose based on your budget and driving needs.
Maintenance Needs
Understanding the maintenance needs of bias and radial tires is crucial for vehicle owners. Proper maintenance can extend tire life and ensure safety. Let’s explore the differences in maintenance requirements for these two tire types.
Wear And Tear
Bias tires tend to wear out faster due to their construction. The layers of cords run diagonally, making them less durable. Radial tires, with their steel belts, offer better resistance to wear and tear.
- Bias Tires: Faster wear, less durability.
- Radial Tires: Slower wear, more durable.
Radial tires provide a smoother ride, reducing uneven wear. Bias tires may develop flat spots if parked for long periods.
Repair And Replacement
Repairing bias tires is often easier. Their simpler construction allows for straightforward fixes. Radial tires, though more durable, can be more challenging to repair.
| Aspect | Bias Tires | Radial Tires |
|---|---|---|
| Repair | Easier | More challenging |
| Replacement | More frequent | Less frequent |
Bias tires may need replacement more often due to their faster wear. Radial tires, with their longer lifespan, require fewer replacements.
Pros And Cons Summary
Choosing the right tire is crucial for your vehicle. Bias and radial tires have distinct benefits and drawbacks. This section provides a clear comparison to help you decide.
Bias Tires Pros And Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Radial Tires Pros And Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|

Choosing The Right Tire
Choosing the right tire is crucial for your vehicle’s performance and safety. Understanding the differences between bias and radial tires helps make an informed decision. Let’s dive into the key factors to consider.
Factors To Consider
- Durability: Radial tires generally last longer due to their construction. Bias tires may wear out faster.
- Performance: Radial tires offer better handling and stability. Bias tires may provide a smoother ride on rough terrains.
- Cost: Bias tires are often cheaper initially. Radial tires might save more in the long run.
- Usage: Radial tires are perfect for daily driving and highway use. Bias tires suit off-road conditions better.
Making An Informed Decision
Consider your driving habits and the terrain you frequently encounter. If you drive mostly on highways, radial tires are a better choice. For off-road adventures, bias tires may offer the necessary support.
| Aspect | Bias Tires | Radial Tires |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Less durable | More durable |
| Performance | Good on rough terrain | Better on highways |
| Cost | Cheaper initially | Cost-effective over time |
| Usage | Off-road | Daily driving |
Always consider your specific needs before making a choice. The right tire improves your vehicle’s performance and ensures safety on the road.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Better, Radial Or Bias Tires?
Radial tires offer better fuel efficiency, longer tread life, and a smoother ride. Bias tires provide stronger sidewalls and better off-road durability. Choose based on driving needs.
How To Tell If A Tire Is Radial Or Biased?
Check the tire sidewall. A radial tire shows an “R” before the rim diameter, while a bias tire shows a “D” or no letter. Radial tires have steel belts, bias tires have layered plies. Radials offer smoother rides; bias tires are stiffer.
What Is A Major Disadvantage Of A Bias Ply Tire?
A major disadvantage of a bias ply tire is its poor traction and handling at high speeds. The tire structure generates more heat, leading to faster wear.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Radial Tires?
Radial tires can be more expensive than bias tires. They have stiffer sidewalls, which may reduce ride comfort. Some models may wear unevenly. They are also less suitable for off-road conditions due to their construction.
Conclusion
Choosing between bias and radial tires depends on your driving needs. Bias tires offer durability on rough terrains. Radial tires provide better traction and fuel efficiency. Each tire type has distinct advantages. Understanding these differences helps you make an informed decision.
Choose wisely based on your vehicle and driving conditions.